EpiOcular: The Future of Toxicology Testing
Challenges of Animal and 2D Testing
Toxicology testing is an essential part of drug development, chemical safety, and consumer product testing. Traditionally, animal testing and 2D cell culture have been the gold standard for toxicology testing, but they have several limitations. The high costs, ethical concerns, and poor predictivity of live animal testing, and the lack of complexity and reproducibility of 2D cell culture makes both methods unreliable predictors of clinical outcomes. With the advancement of in vitro technologies, scientists can now use alternative methods that are more reliable, cost-effective, and ethical. One such method is the use of EpiOcular in vitro 3D Tissues, which is changing the landscape of toxicology testing.
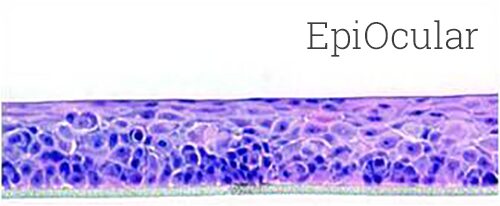
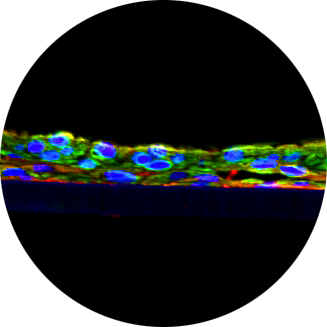
Lab-grown from human cells, EpiOcular in vitro 3D tissues mimic the structure and function of the human cornea. They are used to assess the potential for eye irritation and damage caused by chemicals and other substances. EpiOcular tissues are cultured at the air-liquid interface, which allows them to develop a multi-layered structure that closely resembles the human eye. This structure provides a more accurate representation of the eye’s response to chemicals and other substances than traditional 2D cell cultures.
Advantages of Lab-Grown Human Tissues
One of the advantages of using EpiOcular tissues in toxicology testing is their consistency. EpiOcular tissues are derived from normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK) from a single donor, which ensures consistency in the tissue’s response to chemicals and other substances. This consistency is essential for accuracy in toxicology testing, and with nearly 30 years of demonstrable reproducibility through inter and intra lot data, EpiOcular is the most consistent and reliable platform for evaluating ocular toxicity.
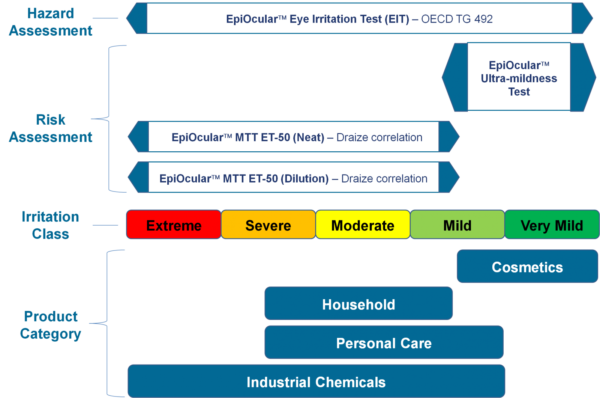
Another advantage of using EpiOcular tissues is their ability to reduce false positives. False positives occur when a substance is incorrectly identified as toxic or harmful. This occurs when traditional 2D cell cultures are used because they do not accurately represent the complex structure and function of the human eye. The complexity of EpiOcular tissues, however, provides a more accurate representation of the eye’s response to chemicals and other substances, reducing the likelihood of false positives.
EpiOcular tissues also have a longer shelf life than traditional 2D cell cultures. EpiOcular tissues are shipped at 4°C on medium-supplemented agarose gels in a 24-well plate. They have a shelf life of up to 4 days at 4°C. This makes them more convenient and cost-effective than traditional 2D cell cultures, which require frequent replacement.
The Future of Tox Testing
The use of EpiOcular tissues in toxicology testing is just the beginning. With the advancement of in vitro technologies, scientists are developing more advanced tissue models to assess the safety and efficacy of drugs and other substances. These advanced tissue models provide a more accurate representation of the human body’s response to chemicals and other substances, leading to more reliable and effective drug development.
In conclusion, EpiOcular in vitro 3D tissues are revolutionizing the field of toxicology testing. They provide a more accurate and reliable method for assessing the potential for eye irritation and damage caused by chemicals and other substances. EpiOcular tissues offer several advantages over traditional 2D cell cultures, including consistency, reproducibility, and the ability to reduce false positives. As in vitro technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see more advanced tissue models to assess the safety and efficacy of drugs. If you are interested in learning more about EpiOcular in vitro 3D Tissues, please click here or reach out to a member of our team.