Reconstruction of novel 3D models of the three parts of small intestine for drug toxicity testing
- TR Number: 1035
- Keywords: EpiIntestinal (SMI-100), duodenum, jejunum, ileum, Digoxin, Elacridar, Loperamide, Sulfasalazine, Ko143, Prazosin, Vinblastine, MK571, Saquinavir, Raloxifene, raloxifene-6-β-glucuronide, midazolam, troleandomycin, Zafirlukast, cytochrome P450, CYP450, CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, , CYP3A4, UGT1A1, UGT1A4, UGT1A10, UGT2B7, ABC efflux transporters, ABCB1, ABCB11, ABCC2, ABCC3, ABCG2, SLCO1B1. SLCO1B3, SLCO2B1, SLC15A1, SLC15A2, SLC16A1, SULT2A1, Carboxylesterase-1, CES1, CES2
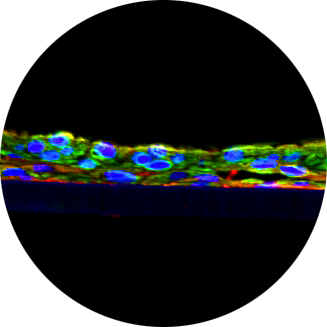
Gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity is a common adverse event that limits pharmaceutical development across diverse therapy areas. The mechanisms of drug induced GI toxicity are often poorly understood, in part due to the lack of physiologically relevant in vitro models that recapitulate the three segments of the small intestine. Traditional in vitro cell cultures utilize the immortalized human colorectal Caco-2 cell line. Even though Caco-2 has been in use for more than 5 decades, it has limitations since Caco-2 is a cancer derived cell-line which lacks the major drug transporters and drug metabolizing enzymes, does not produce fully polarized structural features, and is not predictive of GI toxicity. To mimic the physiology and functionality of the human gut, we previously developed EpiIntestinal, a 3D in vitro small intestinal model utilizing cells derived from the ileum of normal human tissue. However, there is a need by the pharma industry for in vitro 3D models representing the other parts of the small intestine (duodenum and jejunum). Availability of models from the different parts of the small intestine will allow identification of the primary sight of absorption for drug candidates to predict efficacy, risk, and/or dose scheduling to mitigate risk